How Air Filters and Air Purifiers Work ?
How Air Filters and Air Purifiers Work?
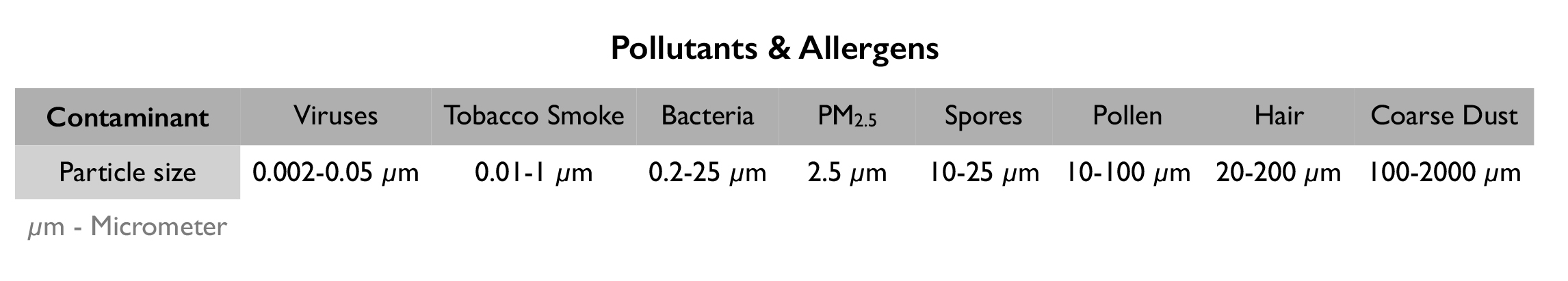
Air filters are devices designed to generate airflow which will partially or completely purify inhaled air. They typically consist of one or more filters, to collectively capture particles of various sizes (Table 1: Common air contaminante sizes).
So how Do They Work?
➡ Contaminated air is drawn into the device
➡ Particles are trapped in the filter media
➡ Clean Fresh Air is released back into the environment
➡ Which mixes back with the contaminated air
➡ Dirty filter cartridges must be manually replaced frequently
What Happens to Contaminated trapped in the Filters?
➡ In most cases, particles remain inside the filter until manually removed.
➡ Large filtration systems require regular maintenance and disposal of collected bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
➡ Given the fact that live micro-organisms may be in filters, removal and disposal should be handled by specialist with proper protective gear.
➡ These Non-Biodegradable filters go into the land fills.
Types of Filters
Some of the commonly used filters are Activated Carbon, Air Washers, EPA, HEPA, and ULPA Filters
Activated Carbon Filters:
Remove substances like: Dust, heavy metals, and toxic chemicals from gases or liquids.
Not effective against: Pathogens or larger dust particles for which it requires pre-filters.
Maintenance Required:
- Contaminants must be flushed out to prevent clogging.
- Activated carbon absorbs up to 20% of its weight—it must be replaced or regenerated.
- Once saturated, “exhausted carbon” must be disposed of to prevent breakthrough contamination.
- Best Use: Removes chemical pollutants & odours (filters particles between 0.0001 µm – 0.001 µm).
Air Washers
Removes: Dust, pollen, and mites from the air using water.
Not effective against: Pathogens, microorganisms, or spores.
How They Work:
- Air is pulled through water, which traps contaminants.
- Clean, humidified air is released back into the room.
Maintenance Considerations:
-
- Water must be changed every 6 months to prevent microbial growth.
- Adding disinfectants can reduce bacterial spread but may result in chemical exposure.
EPA, HEPA, and ULPA Filters
Let’s understand them ?
EPA — Efficiency Particulate Air filter
- EPA are a type of air filter designed to capture particulate matter, specifically those that are 0.3 microns or larger.
- They are commonly used in ordinary ventilation systems, industrial applications, and situations where high efficiency is not necessary
HEPA — Efficiency Particulate Air filters
- HEPA filters are pleated mechanical air filters that trap particles by using a mesh of fine fibers made of glass fiber mats (1-10 µm fiber diameter).
- They are specialised air filters designed to capture a high percentage of airborne particles, including dust, pollen, mould, and bacteria, with a size of 0.3 microns (µm) or larger.
- HEPA filters are used in various applications, including air purifiers, vacuum cleaners, and ventilation systems, to improve air quality.
ULPA — Ultra-Low Particulate Air Filter
- They are highly specialised air filter designed to remove 99.999% of particles 0.12 microns in diameter or larger, making it more effective than HEPA filters for capturing extremely small contaminants.
- ULPA filters are used in commercial air filtration systems to trap extremely small particulate contaminants.
- ULPA filters are used in environments where the highest levels of air purity are required, such as cleanrooms for semiconductor manufacturing, pharmaceutical labs, and other specialised applications.
- ULPA filters are typically more expensive and have lower airflow compared to HEPA filters.
Key Considerations for HEPA Filters:
- HEPA-labeled filters don’t always meet official EU standards—check for compliance with EN 1822-1:2009.
- Most Penetrating Particle Size (MPPS) of these filters are:
- Particles between 0.1 µm – 0.3 µm are hardest to filter.
- This is a weak spot in the filter technology—some particles may pass through.
- Filter replacement requires extreme care to avoid releasing trapped contaminants into the air.
- The non-biodegradable nature of traditional HEPA and ULPA filters contributes to environmental pollution.
- EPA, HEPA, and ULPA filters are generally NOT biodegradable as they are typically made from synthetic materials like fibreglass or plastic.
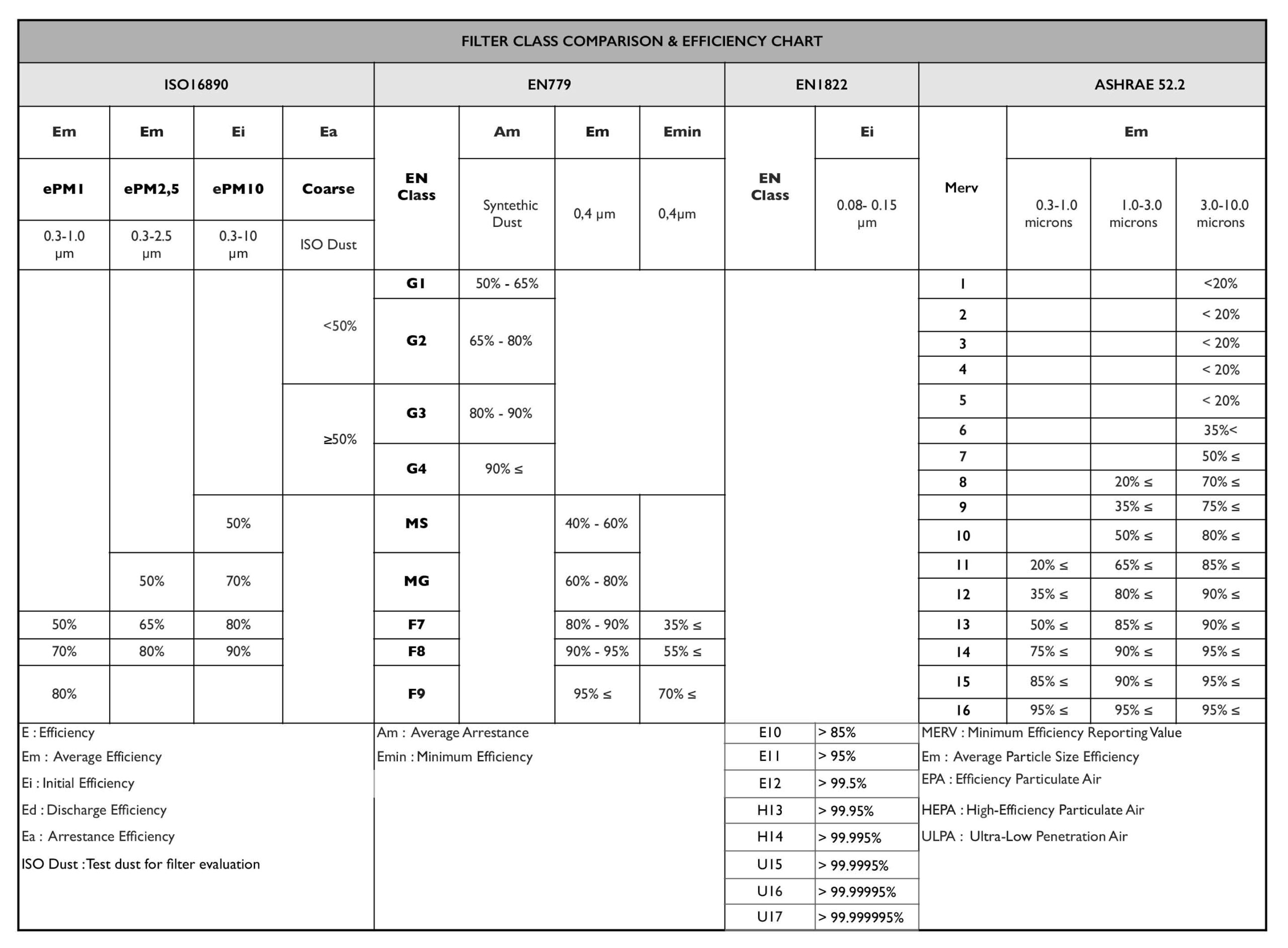
FILTER CLASS COMPARISON & EFFICIENCY CHART (Table 2):
Alternative Air Purification Technologies
Apart from the above filters other air purification methods include:
- Ionizers : A device that releases negative ions into the air, which then electrically charge other particles, causing them to stick to surfaces and settle out of the air, potentially improving indoor air quality.
- Coarse particle and fine dust pre-filters : Pre-filters, which can be either coarse or fine dust filters, are air filters used before other filters (like HEPA) to capture larger particles, extending the lifespan and efficiency of the main filtration system
- Hybrid Filtration Systems : They are a combination of different filtration technologies, such as electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) and fabric filters (bag filters), to achieve enhanced filtration efficiency and address various particle sizes effectively.
AIRsteril® : An Alternative — Filter-Less Air Purification Device
Unlike traditional filtration units, AIRsteril’s bespoke technology does not require all the air to pass though the unit and does not require disposable filter cartridges, thereby reducing maintenance and waste.
How does AIRsteril® Works :
- The indoor air is drawn into the device
Where in a specialised UV lamp along with high-efficiency catalytic grid (nano-TiO₂) eliminate contaminants and purifies the air. - The Clean Air in the form of “Plasma Quattro” comes out and mixes with the Indoor Air and clean the Air in the Air & Decontaminates all Surfaces
Destroying & Eliminating :
- Bacteria
- Viruses
- Pathogens
- Mould & Mildew Spores
- Microorganisms
- VOCs
- Odours including Smoke Smell are permanently neutralised
- Reducing PM2.5
What is “ Plasma Quattro” Technology and how does it work?
The UV lamp interacts with the catalytic grid creating “Plasma Quattro” which is charges clean air with trace elements of :
Ionised Oxygen (O-) : They are negatively charged oxygen atom that has gained an electron, forming an oxide anion: Negative oxygen ions help neutralise airborne pollutants and allergens, improving air quality and reduced oxidative stress
Short lived Triatomic Oxygen (O3 or Ozone) : Commonly refers to as ozone (O3), are naturally occurring, unstable allotrope of oxygen that readily breaks down into diatomic oxygen (O2)
OH Radicals (Hydroxyl Radicals) : They are short-lived neutral form of hydroxide ion (HO–) that often referred to as the “detergent” of the troposphere because it reacts with many pollutants, acting as the first step to their removal. They also has an important role in eliminating some greenhouse gases like methane and ozone
How does It Works ?
Plasma Quattro is slightly heavier than air, they it mixes with the air and settles on surfaces reaching every corner of a room.
It destroys bacteria, pathogens, fungi, and mould spores, VOCs as it goes along mixing with the air and on the surfaces.
Advantages of AIRsteril® Over Traditional filtration systems:
✓ No replacement filters or maintenance required
✓ No filter buildup—prevents microbial growth inside the device.
✓ No chemical-based air fresheners needed
✓ No exposure to harmful cleaning chemicals
✓ No risk of microorganism resistance
✓ More effective than standalone UV or ozone generators
Plus :
✓ Low noise
✓ Portable and wall-mountable
✓ Safe for continuous operation—well below exposure limits

